Early Signs and Symptoms of Brain Tumor!
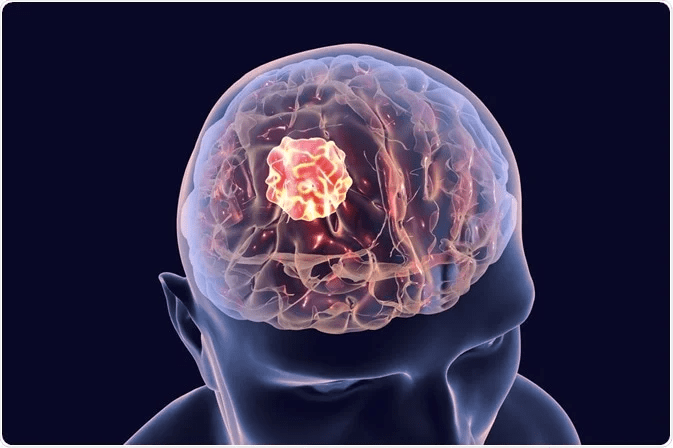
What is Brain Tumor?
Like any other tumor in the body, a brain tumor occurs when at an abnormal rate to form a mass of abnormal cells. These tumors may be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The tumors affect the function of normal brain cells by invading them or causing pressure on normal surrounding brain tissue. These tumors grow over a varying period depending upon whether they are benign or malignant. In India, approximately 45000 people are diagnosed with a brain tumor every year. If left untreated, a brain tumor can either destroy tissue or cause problems in other parts of the body because of the tumor’s pressure on the brain.
Brain tumor symptoms vary from patient to patient, and most of these symptoms can also be found in people without brain tumors. So the only way to know if you have a brain tumor or not is to consult Neurosurgeon and get a brain scan.
Symptoms of Brain Tumor:
- Headaches (usually worse in the morning)
- Disorientation
- Hormonal disorders
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Changes in speech, vision, or hearing
- Anxiety/depression
- Problems balancing or walking
- Confusion
- Difficulty in reading and writing
- Loss of consciousness
- Changes in mood, personality, or ability to concentrate
- Problems with memory
- Muscle jerking or twitching (seizures or convulsions)
- Numbness or tingling in the arms or legs
- Difficulty swallowing
Diagnose:
- Imaging test – This test uses x-rays or radioactive substances to create pictures of the brain. The test results will show a brain tumor in almost all cases.
- MRI scan is one of the best tests available for diagnosing tumors. The images they provide are usually more detailed.
- CT scan – A CT scan uses x-rays to make detailed cross-sectional images of the brain. This scan is usually suggested when MRI is not an option. For instance, people who are overweight or afraid of enclosed spaces.
- PET scan – PET scan uses a special camera to create a picture of areas of radioactivity in the body. This test is likely more helpful for fast-growing tumors than for slower-growing tumors.
Treatment Options:
Surgery:
Surgery is the initial treatment for benign (non-cancerous) brain tumors. These types of tumors can be treated without causing severe damage. However, most malignant (cancerous) tumors require treatment in addition to surgery, such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy. The surgical process results in improving neurological symptoms. It also helps make other brain tumor treatments more effective and improves the patient’s prognosis.
Radiation therapy:
Radiation therapy is typically the option after surgery and possibly along with chemotherapy. It is usually helpful in treating primary brain cancers, which are also called brain tumors. In radiation therapy procedures, high-energy x-rays or other particles destroy tumor cells. Surgeons may use this treatment to slow or stop the growth of the tumor.
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy uses cytotoxic (anti-cancer) drugs to destroy cancer cells. The drugs circulate throughout the body in the bloodstream to stop the growth and division of cancer cells. The purpose of chemotherapy is to destroy tumor cells remaining after surgery and reduce the symptoms of brain tumors. Doctors may suggest chemotherapy alone or in combination with other brain tumor treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy.
Targeted therapy:
Targeted therapy for brain tumors works to target particular pathways or irregularities in brain tumor cells involved in tumor growth. This treatment is mainly an option for patients with a tumor recurrence after previous brain cancer treatments. Targeted therapy blocks the growth and spread of tumor cells while limiting the damage to healthy cells. Consult a Neurosurgeon immediately if the symptoms of a brain tumor shows. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications as a tumor grows and puts pressure on the skull and brain tissue.