Leg Weak point After Microdiscectomy
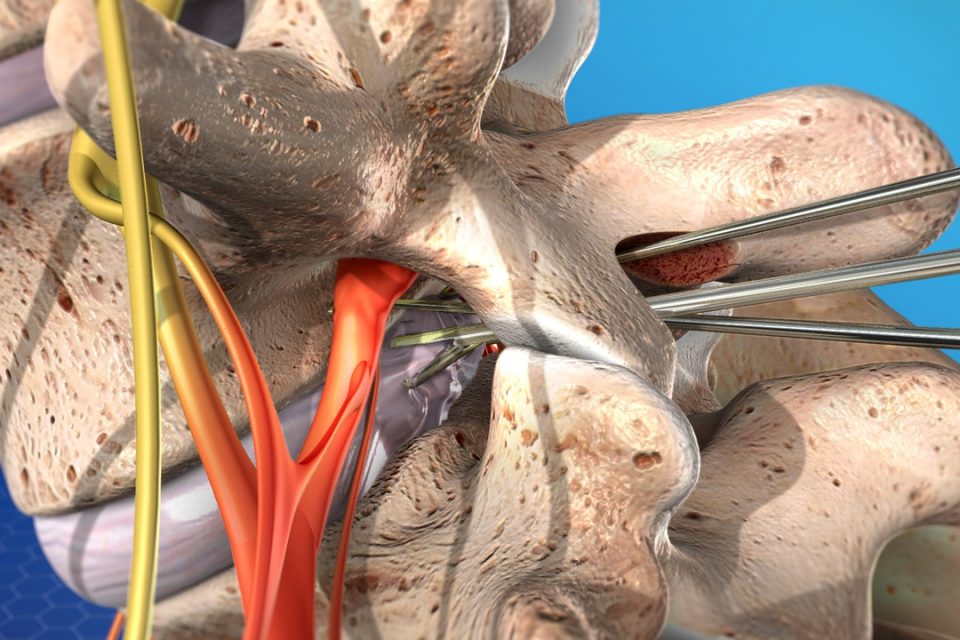
For those suffering from sciatica, conventional treatments such as bodily therapy chiropractic treatment, non-surgical decompression is usually enough. Minimally-invasive microdiscectomy is an usual surgical procedure that is performed on those who’s pain isn’t being relieved through conventional methods or those patients who exhibit extreme symptoms reminiscent of urinary incontinence, which require swift intervention.
The most common reason for sciatica is disc herniation in the backbone of the lumbar region. When the outer ring of the disc becomes weaker the fluid inside the disc’s middle starts to leak out and can cause irritation to nerves that exit the backbone. The sciatic nerve’s roots exit the backbone through the vertebrae L4 and S3 to the S3. Nerve irritation is characterized by acute, radiating pain that radiates starting at the lower part of the spine and radiating towards the legs. a muscle weak spots and an numbness.
Microdiscectomy is the process of removing the disc’s small piece of material that is responsible for impinging on the nerve. Patients who undergo surgery discover that even though the pain ranges increase, power isn’t returned to the muscles of the leg affected.
The success rate for microdiscectomy and other backbone surgery procedures are estimated to be in the range of 95%, according to surgeons. But, these numbers usually indicate that the surgeon had a good success when removing a disc or bones were fused during the process of spinal fusion. The exact amount of sufferers who have been reduced is not always included in the scope of a procedure’s effectiveness.
A review of 91 patients who suffered from disc herniation and leg paresis (slight weak spot or paralysis) that underwent microdiscectomy, confirmed that the success rate for power restoration, were reduced by 95 percent. The majority of patients in the study had recovered power in the affected leg after a year following the surgery. Although this is an overwhelming majority however, nearly a quarter of the patients did not regain their power, which is an impressive percentage.
Microdiscectomy is generally successful in alleviating pain, but it may not reverse the damage to nerves that was done earlier than the time of the procedure. In the event that your sciatic nerve suffered injury that impeded its capacity to send sensory and motor impulses through the leg, it will not be healed immediately following the surgery. Due to this, if you have a muscle weakness area it is unlikely that microdiscectomy will be an option that is more likely than conventional solutions to relieve nerve impingement. Traction, decompression and training treatments should be considered thoroughly prior to considering a surgery.
Nerve Regeneration
The damage to the nerve is usually permanent There is no standard solution to regenerate the sciatic nerve once injury occurs. Experiments with stem cells treatment and the progress issue cure are viable options, but access to them is not permitted. The best bet to try these treatments is to look for research trials to participate in or travel to another country for treatment.
Consumption of Omega-3 fatty acids in any form, be it foods or supplements in the diet may help to restore nerves quick after injury.
The stimulation of nerves with electrical currents can aid in their regeneration and restoration. This method was tested on sciatic nerves that were damaged in rats and proved to stimulate regeneration. Ask local physical therapists, chiropractors, and other health specialists about the possibility of effective electrical stimulation within your area.
The microdiscectomy procedure is not more likely to alleviate severe leg weakness, as it’s typically caused by nerve damage. Although it is essential to determine the cause of pain in the sciatic nerve surgery is likely not the most effective option due to the cost as well as the time required to heal and the risks. Although nerve damage that is severe tends to last forever however, there are innovative methods for regenerating nerves being investigated.