The Oligodendroglioma Brain Tumor Explained
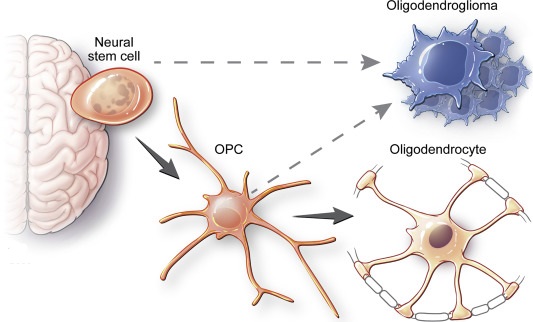
Oligodendroglioma
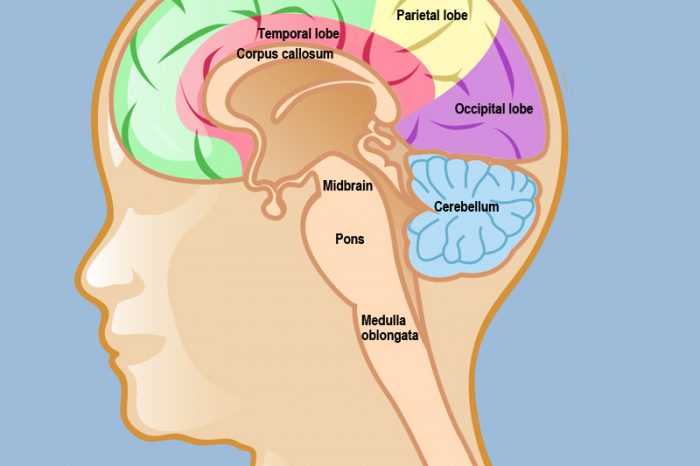
The oligodendroglioma is a rare tumor that develops in the brain. It is created by the cells located in the connective tissue that surrounds the brain’s nerve cells. The symptoms that the patient experiences are heavily dependent upon the tumor’s location.
While more common among the adult population, these cells have been found in children. The oligodendroglioma tumor is considered to grow at an extremely slow rate. This type of tumor accounts for approximately 3% of all tumor diagnoses in the United States population. It has been established that males are more prone to this condition than females.
Symptoms of the Oligodendroglioma Tumor
Individuals that experience the oligodendroglioma tumor may endure a multitude of symptoms. The symptoms experienced are heavily dependent upon the exact location and general size of the tumor. In most instances, the following symptoms are identified in patients suffering from this condition:
• Many individuals will start to experience headaches. In most cases, as the tumor progresses in size, the headaches will progress in severity.
• Many individuals may experience behavioral-based changes. These changes may include a marked personality change, high levels of irritability, depression, and even aggression.
• In some cases where an oligodendroglioma tumor is present, cognitive challenges occur. These challenges may include problems with concentration, complications with memory, and similar issues.
• There are many cases where sufferers of this type of brain tumor will experience motor function complications. Examples include experiencing weakness and paralysis in the body, walking challenges, speaking issues, and similar types of issues.
• Many may start to have mild to severe seizures that directly result from the tumor that is growing in, on, or around the brain.
• Problems with the bowels and bladder may be experienced when an individual suffers from this type of tumor.
Treatments
Many treatments may be necessary to relieve an individual of the symptoms they experience with this tumor type. Medical professionals typically determine the course of treatment by the grade associated with the tumor itself. Surgery may be considered for those with only a benign tumor with minimal symptoms.
Typically, the individual will be monitored after the surgery to determine if the tumor returns or makes an attempt to return and spread. For those who suffer from more serious complications due to their tumor, radiation may be required to ensure that the tumor does not return. Many individuals may also have to undergo chemotherapy sessions as a course of treatment after having surgery for this type of tumor.